What Are Backbone Cables?
Published: January 25, 2025
Backbone cables are like the main highways of a network. They connect smaller networks and allow data flow between different devices, buildings, or locations to flow smoothly and quickly. These cables are critical for businesses, data centers, and even the Internet to work efficiently. Without them, transferring data over long distances would be slow or impossible.

What is Backbone Cable?
Backbone cables are high-capacity cables that transmit large volumes of data across long distances in networks. They provide the primary connection between servers, switches, and other critical devices.
Types of Backbone Cables
Backbone cables come in various types, each suited for specific purposes. Below are the most common types with examples:
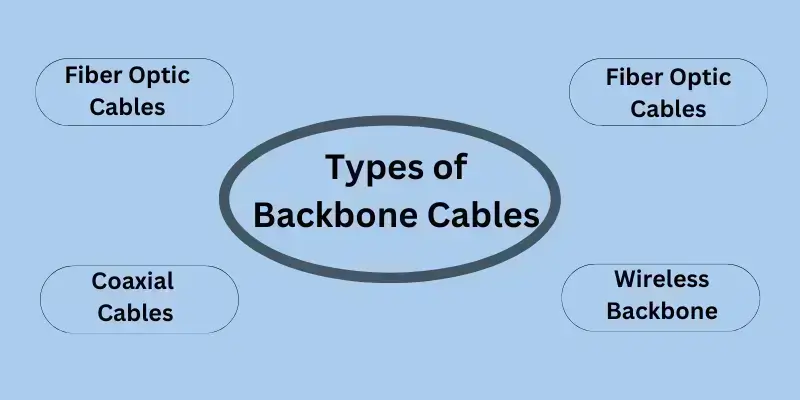
1. Fiber Optic Cables
These use light signals to transfer data quickly over long distances without losing quality.
Example
Used by large companies, internet service providers, and submarine cables connecting continents.
2. Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables have a copper core surrounded by insulation and are often used in older networks. They are slower than fiber optics but still effective in smaller setups.
Example
Cable TV networks and older broadband internet services.
3. Twisted Pair Cables
These cables consist of pairs of wires twisted together to reduce interference. They are commonly used in home and small office networks.
Example
Ethernet cables like Cat5e and Cat6 are used to connect computers and routers.
4. Wireless Backbone
Radio or satellite signals connect networks instead of physical cables. This method is ideal for remote or temporary setups.
Example
Used in rural areas or disaster recovery scenarios where installing cables is impractical.
Role of Backbone Cables in Networking
Backbone cables act as the central connection point in a network. They link smaller networks (like office departments or branches) and allow them to communicate and share data seamlessly. For example, in a university, backbone cables connect all the departments, ensuring smooth access to shared resources like servers and the Internet.
Advantages of Backbone Cables
Fast Data Transfer
Backbone cables allow large amounts of data to move quickly between systems, making them essential for businesses and service providers.
Scalability
They can handle growing network demands as businesses expand.
Reduced Network Delays
Backbone cables minimize delays, even when managing high traffic or covering large distances.
Challenges in Using Backbone Cables
Cost
Installing and maintaining backbone cables, especially fiber optics, can be expensive.
Installation Complexity
Setting up backbone cables requires skilled professionals and detailed planning.
Physical Vulnerability
Cables can be damaged by weather, accidents, or wear and tear, leading to network disruptions.
Common Applications of Backbone Cables
1. Data Centers
Backbone cables connect servers and storage devices, enabling fast and reliable data access.
2. Telecommunication Networks
These cables facilitate phone calls, text messages, and internet connectivity.
3. Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
ISPs use Backbone cables to deliver high-speed internet to homes, businesses, and offices.
4. Cloud Computing
They connect cloud servers to ensure smooth data access and transfer for cloud services.
5. Enterprise Networks
Backbone cables link various branches or departments of an organization, ensuring quick and reliable internal communications.
6. Educational Institutions
Schools and universities use these cables to connect different parts of their campuses, ensuring fast internet for students and staff.
7. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
These cables help distribute web content, such as videos and media, efficiently to end users, minimizing load times.
8. Smart Cities
Backbone cables support IoT infrastructure, connecting various sensors and systems for smart city functions like traffic control and public safety.
9. Broadcasting
Backbone cables connect broadcasting stations to transmission equipment, ensuring smooth media delivery.
A backbone cable is a physical medium (like fiber-optic or coaxial cables) that transfers large volumes of data between network devices.
On the other hand, a backbone network is the overall infrastructure of interconnected systems (cables, routers, switches, and protocols) that ensure smooth data flow across local or global networks. The cable is the hardware; the network is the complete system!
Future of Backbone Cables

Advancing Fiber Optics
Future innovations will make fiber optics faster, more affordable, and widely accessible.
Supporting 5G and IoT
As 5G and IoT devices become more common, backbone cables will effectively manage the increased data flow.
Eco-Friendly Solutions
Research focuses on making backbone cables more sustainable to reduce environmental impact.
You may also like these posts:
Conclusion
Backbone cables are the backbone of modern communication and data transfer. They ensure data travels quickly and reliably across networks, whether for businesses, homes, or global connections. With advancements in technology, backbone cables will continue to play a critical role in building faster and more efficient networks in the future.
No, backbone cabling vs. horizontal cabling serves different purposes. Backbone cabling connects major network segments across long distances, while horizontal cabling links individual devices within a specific area to the backbone. Both are essential for a complete network infrastructure.