What is a Local Area Network (LAN)? Simple Guide to LAN
Published: October 23, 2025
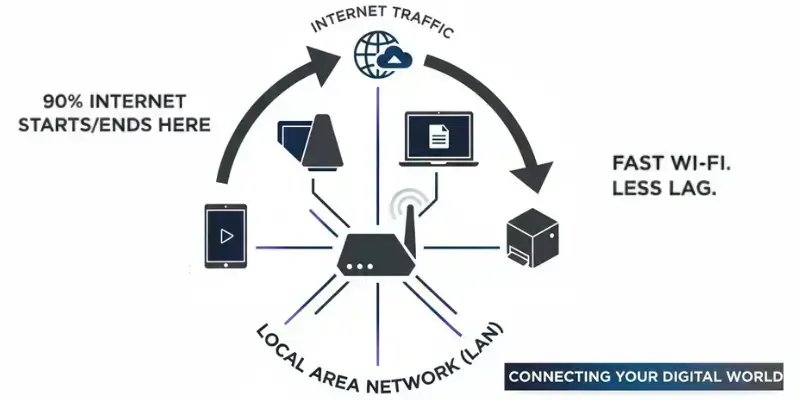
A Local Area Network (LAN) runs almost every house and office. More than 90% of all internet traffic starts or ends inside a LAN. These small, fast networks are why you can stream a movie and print a paper at the same time. A LAN connects your devices right where you are. Understanding this basic network is key. It helps you get faster Wi-Fi and fewer slow moments.
What is a Local Area Network (LAN)?
LAN stands for Local Area NetworkA LAN connects devices in one small area. It is the easiest network to set up and use. The word “Local” means it only works over a short distance. Think of a network that stays inside one building or one small campus.
Example
Your home network is a LAN. It is the system that allows your phone, laptop, and smart TV to all communicate with your Wi-Fi router. It works the same way in a school or a small office. All the computers there use a LAN to share printers and files.
Why You Need to Know This
Many people use a LAN every day without giving it a thought. If you understand your LAN, you can make your internet better.
- Fast Sharing: A LAN lets you share files and resources instantly. This is great for teamwork and accomplishing tasks efficiently.
- Easy Access: It provides easy access to a shared internet connection.
- Fix Slow Wi-Fi: Knowing how your LAN works allows you to troubleshoot and resolve slow Wi-Fi issues. You can share large files much faster.
How a LAN Works: The Three Simple Steps
Every Local Area Network (LAN) works by following three simple steps. Think of it as a small, fast data delivery service.
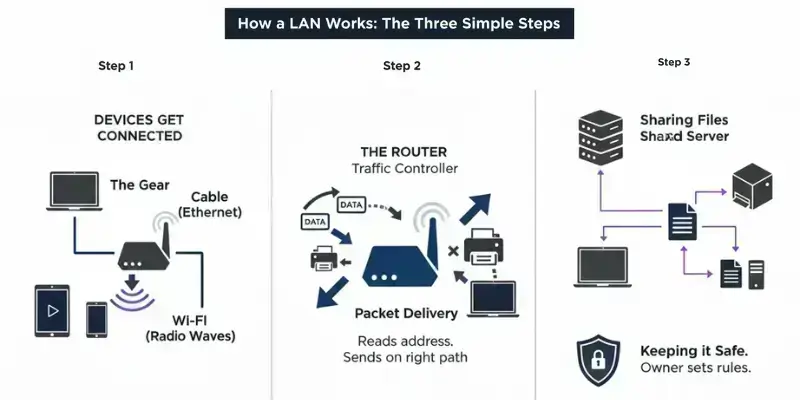
Step 1: Devices Get Connected
First, you need things to talk to the network.
The Gear
These include items such as your computer, phone, and printer.
The Link
They connect using a cable (Ethernet) for the fastest link or by Wi-Fi (radio waves) for easy, wireless access.
Step 2: The Router Manages Traffic
Your router or switch is the network’s brain and traffic controller.
Its Job
It ensures that when your computer sends information, it reaches the intended destination. It prevents data from being sent to every single device.
Packet Delivery
All information moves in tiny pieces called data packets. The router reads the address on each packet and sends it on the right path—fast and safely.
Step 3: Information is Shared Safely
LANs are great for sharing resources inside a small area.
Sharing Files
In many offices and schools, a main computer, known as a server, holds important files and software. Any device on the LAN can get these files without having to download them from the Internet.
Keeping it Safe
The network owner (like you) sets simple rules. This keeps private files safe. It stops people who are not on the LAN from using your private network.
Real-Life Example
Imagine a school’s computer lab. All the PCs are linked by a LAN.
When a student hits “print,” the tiny data packets move through the router to the printer in just seconds. The student can also open files from the school server instantly!
Actionable Tip: Place the Router Smartly
Where you put the brain of your LAN matters a lot.
- Place your router in a central location in your house. Keep it off the floor. Do not hide it in a cabinet.
- Why? The Wi-Fi signal will reach all your devices better. This simple step can fix slow Wi-Fi in rooms that are far away.
Types of LAN: The Different Ways to Connect
You might think every Local Area Network (LAN) is the same. However, the way devices are set up allows the LAN to function in different ways. These setups are called topologies. They tell you the shape and flow of the network.
Here are the main types of LAN setups and who should use them:
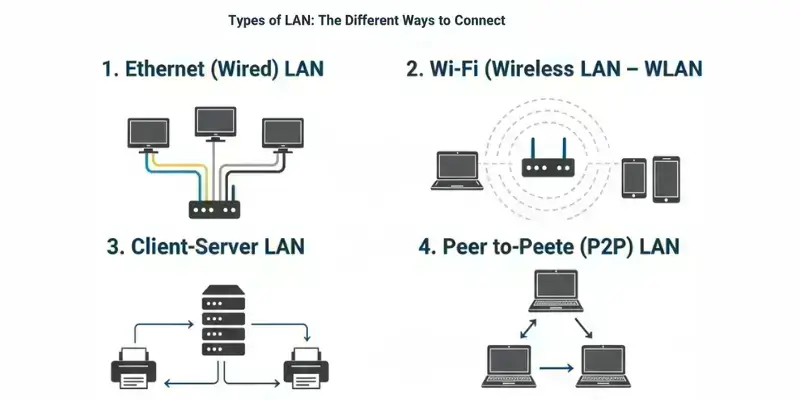
1. Ethernet (Wired) LAN
What it is
This LAN uses yellow, blue, or gray Ethernet cables. It is the classic, most reliable LAN type.
Best for
Power users and gamers. It gives you the fastest speed and the steadiest connection with no lag.
2. Wi-Fi (Wireless) LAN – WLAN
What it is
This is the most common LAN today. It uses radio waves (Wi-Fi) to connect devices without the need for cables.
Best for
Every home user.
It is easy to use and lets you walk around with your phone or laptop while staying connected.
3. Client-Server LAN
What it is
This LAN has one main computer (the server) that stores files and manages everything. The other devices (clients) request what they need from the server.
Best for
Small to mid-sized offices. It is great for sharing data safely and controlling who can access files.
4. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) LAN
What it is
In this simple LAN, every computer is equal. There is no central server. Computers share files directly with each other.
Best for
A tiny home network (two or three PCs). It is inexpensive and easy to set up, but harder to keep secure if you add many devices.
Historical Note
In the past, LANs were mostly wired, using bulky cables and limited speeds.
Today, wireless LANs (WLANs) dominate — offering faster, simpler, and more flexible setups for modern users.
Quick Suggestion
Choose Wired LAN if you need speed and reliability.
Choose Wireless LAN if you prefer mobility and easy setup.
What Equipment Is Needed to Set Up a LAN?
Setting up a Local Area Network (LAN) doesn’t need fancy tools. You just need a few basic devices that help your computers, printers, and phones connect and share data easily. Let’s look at what LAN Equipment you’ll need.
1. Router
A Router connects all your devices and manages how data moves between them.
It also links your LAN to the internet if needed.
Think of it as the “brain” of your network.
2. Switch
A Switch helps connect multiple wired devices inside your LAN — like computers, printers, or servers.
It ensures data is directed to the correct location without slowing things down.
Used more in offices than in small homes.
3. Network Cables (Ethernet Cables)
These are the wires that carry data between your devices, router, and switch.
They come in different types (like Cat5e or Cat6), depending on how fast and far you need data to travel.
Tip: Wired connections are generally faster and more stable than Wi-Fi.
4. Network Interface Card (NIC)
Every computer or device needs a NIC to connect to a network.
It’s built in on most laptops and desktops today.
It’s like your device’s network ID badge.
5. Modem (Optional)
If you want internet access along with your LAN, you’ll need a Modem.
It connects your LAN to your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
6. Access Point (For Wireless LANs)
If you’re setting up a Wi-Fi-based LAN, you’ll need one or more Access Points to send wireless signals around your space.
7. Server (Optional but Useful)
In large networks, a Server stores and manages files, printers, and user access.
In a small home LAN, your main computer can act as a simple server.
Quick Example: School Computer Lab
In a school computer lab, these tools work like this:
- The Router connects all computers to the internet.
- A Switch manages connections between devices.
- Ethernet cables link each computer to the switch.
- A Server stores shared learning files for all students.
Tip for Home LAN
If you’re setting up a LAN at home, you might only need a router and your Wi-Fi-enabled devices—simple and quick!
When Is a LAN the Best Choice?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is not the right fit for every job. It is perfect for connecting things in a single, compact space. You should use a LAN when you need fast speed and simple sharing over a short distance.
Here are the best times to use a LAN:
1. Your Home Network
Every modern home uses a LAN.
Need
You need all your devices to share one fast internet connection.
Example
Your smart TV streams a show. Your laptop works on a file. Your phone downloads an app. The LAN ensures that all devices work simultaneously without slowing down.
Why LAN Wins
It offers the easiest setup and the fastest speed inside your walls.
2. Small Office or Floor
A LAN works perfectly for small businesses or a single floor of a large building.
Need
Employees must share files, use one central printer, and access software stored on a local server.
Example
Five people are working in the same room. They can send huge design files to each other in seconds.
- Why LAN Wins: It keeps important business files safe and local. Data does not have to travel far, so work is faster.
3. School Labs and Libraries
Schools utilize LANs to manage multiple users simultaneously.
Need
Many computers must access the same learning tools and software simultaneously.
Example
A computer lab has 30 student computers. All the students can use the shared network printer instantly.
Why LAN Wins
It makes sharing expensive equipment (like printers) easy and cheap for the whole school.
4. Gaming and Media Centers
If you are a serious gamer or media creator, a LAN is a must.
Need
You need a zero-lag, steady connection for high-speed activity.
Example
Hosting a LAN party where everyone plugs their computer into the same switch for the best gaming speed.
Why LAN Wins
Wired LAN connections are the fastest possible. They eliminate the delay associated with Wi-Fi.
When NOT to Use a LAN
If you need to connect offices in two different cities or countries, a LAN will not work. For that, you would need a much larger network, such as a WAN (Wide Area Network).
Actionable Tip
If your job or hobby requires high speed and steady reliability, you should always use a wired LAN connection (Ethernet cable) for that device.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LAN
A Local Area Network (LAN) enables faster sharing, communication, and teamwork in small areas, such as homes, offices, or schools.
But just like any technology, LAN has advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages (The Good Things)
Fastest Speed
Data moves very quickly because the distance is short. (Great for Gaming!)
Low Cost
The equipment (such as routers and cables) is inexpensive to purchase.
Easy Setup
Installation and setup are simple in a home or small office.
Data Security
Your files are stored securely within your building. It is easy to control who can see them.
Simple Sharing
Devices can easily share a single printer and big files. (Great for Work and Study!)
Central Storage
You can store all important files on one main computer (server).
Disadvantages (The Limits)
Limited Range
The network only works in a small area (one building or room).
Setup Time
Setting up a wired LAN with numerous cables can be time-consuming.
Maintenance
A single faulty wire or broken switch can disrupt the entire network.
Security Risk
If a bad person gets inside your LAN, they can access all devices quickly. (Compared to a WAN, where access is much harder).
How Do LANs Relate to the Rest of the Internet?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is like your small, private world inside the huge universe of the Internet.
It connects your local devices — like laptops, phones, and printers — while the Internet connects millions of LANs across the globe.
Let’s see how they work together.
1. LAN Is Your Starting Point
Every time you go online, your device first connects to your home or office LAN.
Example: Your laptop joins your Wi-Fi network — that’s your LAN.
2. The Router Acts as a Bridge
Your router links your LAN to your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
It sends and receives data between your local devices and the wider Internet.
Without the router, your LAN stays private and offline.
3. The Internet Connects Many LANs Together
The global Internet is basically a network of networks — millions of LANs linked through routers, modems, and ISPs.
So when you send an email or visit a website, your LAN communicates with another LAN somewhere else in the world.
4. LAN Provides Security and Speed Inside
While the Internet connects everyone, your LAN keeps things local, private, and fast.
You can still share files or print documents even when the Internet is down — because those actions happen within your LAN.
Quick Example
When you stream a movie:
- Your LAN connects your smart TV to your Wi-Fi.
- Your router sends the request to your ISP.
- The Internet delivers the movie from the streaming server back to your LAN.
In Short Difference between LAN and internet
LAN = Your local connection.
Internet = A Global network of many LANs.
Router = The bridge that joins them together.
LAN Topologies: The Shapes of Your Network
A LAN topology illustrates the connections between devices in a local area network (LAN). Think of it as the layout or map of your network. The shape you choose affects your LAN’s speed, reliability, and overall cost.
Here are the most common shapes:
1. Star Topology (The Star Shape)
How it Connects
Every device connects to a central piece of equipment (such as a Switch or Hub).
Pros
Easy to manage and fix. If one device fails, the others continue to function.
Cons
Needs more cable than Bus or Ring. If the central Switch fails, the whole network stops.
Best for
Homes and most small offices.
2. Bus Topology (The Line Shape)
How it Connects
All devices share a single, long main cable.
Pros
Needs the least amount of cable. It is cheap to set up.
Cons
Best for small networks, but it slows down if too many users connect. It is hard to find a broken connection.
Best for
Very small and simple networks (now rarely used).
3. Ring Topology (The Circle Shape)
How it Connects
Each device connects only to the two devices next to it, making a circle.
Pros
Data moves very quickly in one direction.
Cons
Data travels in one direction, but the network is weaker if just one link breaks. Adding new devices is difficult.
Best for
Used in some high-traffic, specialized networks.
4. Mesh Topology (The Fully Connected Shape)
How it Connects
Every device connects directly to every other device.
Pros
It is super reliable—data can always find a path. If one path fails, another path works.
Cons
Expensive and complex to set up due to the many wires needed. It is very hard to install.
Best for
High-reliability networks (like hospitals or military systems).
5. Tree Topology (The Combined Shape)
How it Connects
This shape is a mix of the Star and Bus shapes. It is used in large organizations.
Pros
Good for expansion, meaning you can easily add more devices or groups.
Cons
It can be tricky to maintain. The whole network depends on the main Bus line.
Best for
Large corporate networks or university campuses.
In Short
Every topology has trade-offs. Small home networks often use a Star Topology. Large offices may combine Tree or Mesh for better stability.
The file is now fully updated with clear Pros, Cons, and Best For sections for all five topologies!
We have covered every major topic for your blog post. We are ready for the final section: the Conclusion and Actionable Tips. Are you ready to write that ending?
LAN Security
A Local Area Network (LAN) carries sensitive data, such as files, passwords, and messages; keeping it secure is very important. Without proper protection, anyone connected to the same network could steal data, spread malware, or disrupt operations.
Why LAN Security Matters
Even small networks can face big risks.
If one device is infected with a virus, it can spread across the LAN and affect all connected systems.
Hackers can also break into poorly protected networks to steal information or misuse internet access.
So, LAN security ensures three main things:
Confidentiality: Only authorized people can see or access data.
Integrity: Data remains safe and unaltered during transfer.
Availability: The network stays stable and accessible when needed.
Common LAN Security Measures
Here are some effective ways to secure a LAN:
1. Strong Passwords
Always set complex, unique passwords for routers, Wi-Fi, and shared devices. Avoid using easy ones like “123456” or your name.
2.Firewalls
These act as barriers between your LAN and the outside internet, blocking harmful traffic and filtering unauthorized access.
3. Antivirus Software
Every device connected to a LAN should have updated antivirus protection to detect and remove threats.
4. Data Encryption
Use protocols like WPA2 or WPA3 on Wi-Fi routers so transmitted data remains unreadable to outsiders.
5. Access Control
Allow only trusted devices and users to connect. Many routers offer MAC address filtering for this purpose.
6. Regular Updates
Keep routers, switches, and computers updated to patch any security loopholes.
7. Network Monitoring Tools
Tools like Wireshark or PRTG help detect unusual activities early, such as unauthorized access attempts or bandwidth misuse.
Common LAN Security Threats
- Unauthorized Access – Strangers connecting to the network without permission.
- Viruses and Malware – Infected devices are spreading malicious files across the network.
- Data Theft – Sensitive files are being copied or stolen from shared folders.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks – Hackers intercepting data between devices.
- Denial of Service (DoS) – Overloading the network so it becomes slow or crashes.
Example
In an office, imagine an employee connects a personal laptop infected with malware.
If the LAN isn’t protected, that virus could spread to shared drives, causing data loss.
But with strong access control, antivirus, and encryption, the threat can be stopped before it spreads.
Pro Tip
Although a LAN may feel private, it’s never fully isolated.
Always treat it with the same care as the Internet — secure passwords, regular updates, and limited access.
A few preventive steps can save your whole network from serious harm.
How Cloudflare Protects LANs
While Cloudflare is best known for protecting websites on the internet, it also plays a big role in keeping Local Area Networks (LANs) safe — especially for offices, schools, and remote teams that connect through the cloud.
A LAN, on its own, can only protect devices inside its local area. But when data travels beyond it, for example, when employees access cloud apps or remote servers, Cloudflare adds an extra layer of defence.
1. Shields LAN from External Threats
Cloudflare’s firewall and DDoS protection block attacks before they even reach your local network.
It filters harmful traffic, bots, or malware coming from outside sources — keeping your LAN devices safe.
Example
If someone attempts to flood your office network with fake traffic (a DDoS attack), Cloudflare absorbs and filters it in the cloud, ensuring your LAN remains fast and stable.
2. Secures Remote Access
With Cloudflare Zero Trust, users can securely connect to their LAN from anywhere — at home, in a café, or in another city — without using risky VPNs.
It verifies every user and device before allowing access, ensuring that only trusted individuals can access your local files or apps.
Even if hackers get the password, they can’t enter without identity verification through Cloudflare.
3. Protects Internal Apps and Data
Many offices run internal web apps (like dashboards or tools) within their LAN.
Cloudflare’s Access service hides these apps behind secure gateways, so they’re invisible to outsiders.
It ensures only verified users within your organization can open them.
4. Monitors and Filters Network Traffic
Cloudflare provides real-time analytics and filters that show who’s using your network and what’s happening inside it.
This helps IT teams identify suspicious activity early, such as sudden data transfers or unusual login attempts, and block them immediately.
Example
Think of Cloudflare as a protective bubble around your LAN.
Your local devices handle daily tasks like file sharing or printing, while Cloudflare guards the entry points that connect your LAN to the internet.
In Simple Words
- LAN security protects what’s inside your local area network (LAN).
- Cloudflare security protects your network’s connection to the outside world.
- Together, they make your system both fast and safe.
What Is a Virtual LAN (VLAN)?
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a special type of network that divides one physical LAN into smaller, separate parts through software instead of extra cables.
In a normal LAN, every device is part of the same group. But in a VLAN, you can create multiple groups within the same network — even if the devices aren’t physically next to each other.
Example
Imagine your office LAN connects 20 computers.
You can make:
- One VLAN for the HR department
- Another VLAN for Finance
- And another for IT support
- Even though all computers use the same cables and switches, each group works in its own “private lane.” Data from HR stays separate from Finance, keeping things organized and secure.
Comparison Table: Wired LAN vs Wireless LAN vs Virtual LAN
| Aspect | Wired LAN | Wireless LAN (WLAN) | Virtual LAN (VLAN) |
| Connection Type | Uses physical Ethernet cables | Uses Wi-Fi signals | Uses software-based virtual grouping |
| Mobility | Limited (fixed connections) | High (move freely within range) | Depends on network setup |
| Speed | Very fast and stable | Moderate, can vary with distance | Depends on base LAN’s speed |
| Security | Very high (no wireless signal leaks) | Moderate (can face Wi-Fi attacks) | Very high (isolated virtual groups) |
| Setup Cost | High (requires cables and switches) | Low (only needs router/access points) | Moderate (needs VLAN-capable switches) |
| Installation | More complex and time-consuming | Easy and quick setup | Needs software configuration |
| Flexibility | Low (physical connections) | High (wireless freedom) | Very high (software-based setup) |
| Maintenance | Simple but hardware-heavy | Easier but needs signal checks | Managed through network software |
| Best For | Offices, schools, data centers | Homes, small offices, cafés | Enterprises, secure organizations |
| Example | PCs connected with Ethernet cables | Devices linked via home Wi-Fi | Departments separated virtually on one LAN |
Comparison Table: LAN vs WAN
Here’s a quick comparison table to help you easily see how LAN vs WAN differ
| Aspect | LAN (Local Area Network) | WAN (Wide Area Network) |
| Full Form | Local Area Network | Wide Area Network |
| Coverage Area | Small area – one home, school, or office | Large area – covers cities, countries, or even the world |
| Ownership | Usually owned and managed by one person or organization | Shared or managed by service providers (like ISPs) |
| Speed | High speed (up to 1 Gbps or more) | Slower due to long distances |
| Connection Type | Uses Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi | Uses telephone lines, fiber optics, or satellites |
| Setup Cost | Lower (simple devices like routers and switches) | Higher (needs complex infrastructure) |
| Data Transfer | Quick and secure within a local area | Can face delays due to distance |
| Reliability | Very reliable | Can be affected by network congestion |
| Example | School computer lab or home Wi-Fi network | The Internet or a bank’s nationwide network |
Conclusion: Your Fast, Smart Network
So, in this article, we’ve covered Local Area Networks (LANs) in detail. Do you truly know if your router is safe right now? We learned how this simple system is the engine that powers your home and office internet. We looked at the few devices you need, the smart shapes (topologies), and how to protect it from bad people. The biggest mistake is never updating your router’s software.
Your actionable review is to check the router’s website today for the newest version.
My final recommendation is to always use an Ethernet cable for your most important devices, such as gaming PCs, because it prevents slow speeds.
Check your router’s website now for the newest updates, and share this article with a friend who needs a safer, faster network!
You may also like these posts:
FAQs About Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN, or Local Area Network, is a network that connects computers and devices within a small area, such as a home, school, or office. It helps share data, the internet, and printers easily.
A LAN connects local devices, while the Internet connects networks worldwide. Think of LAN as your “inside” network and the Internet as the “outside” world.
You’ll need a router, a switch, Ethernet cables (for wired LAN), and devices such as computers or printers. For wireless LANs, you’ll use a Wi-Fi router or access point.
It can happen if too many users are connected, cables are damaged, or your router is outdated. Restart your router and check the cable connections to resolve the issue.
Yes! Many homes and offices use a mix of wired LANs for stability and wireless LANs for mobility. They work together through the same router.
Use strong passwords, update your router regularly, and avoid sharing network access with unknown devices. You can also enable firewalls or use tools like Cloudflare for extra protection.
A VLAN divides one physical LAN into smaller virtual groups using software. It helps improve security and organize traffic inside big networks.
No, LANs can function independently of the Internet. You can still share files, print documents, or play games locally between devices.
Modern LANs can transfer data at speeds ranging from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps or more, depending on the type of cables and switches used. Wired LANs are usually faster than wireless ones.
Anyone who wants to connect multiple devices in one place — homes, offices, schools, or small businesses. It’s perfect for teamwork, file sharing, and local communication.