LAN vs WAN: What’s Good and What’s Really Bad About Both
Published: October 17, 2025
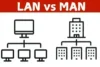
You may notice that the internet experience at home is different from that in larger offices or schools. This is because they use different types of networks: LAN (Local Area Network) and WAN (Wide Area Network).
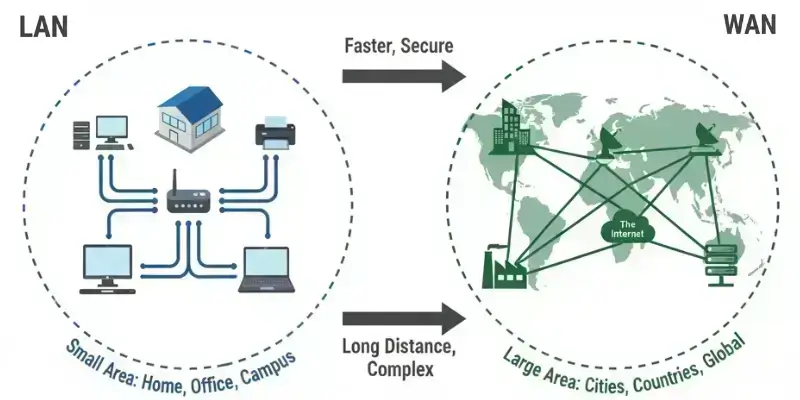
A LAN links computers and devices within a small area, like a room, office, or school. It’s quick and stable, perfect for sharing data or printers nearby. Unlike a WAN, a LAN typically covers short distances, making it less suitable for connecting multiple locations.
A WAN connects devices that are far apart, even across countries, using the internet or private connections. Unlike a LAN, a WAN is ideal for large organizations that require long-distance communication. But it can be costly and more complex to manage.
Many people mix up these network types because both connect devices, but they serve different purposes. In the following sections, we’ll explore how each type works, look at their unique strengths, and clarify when to use each.
Before diving into those details, let’s first clarify what we mean by LAN and WAN. This will provide helpful context for what’s next.
Definitions of LAN and WAN
LAN (Local Area Network)
A LAN (Local Area Network) connects computers and devices within a small area, such as a home, school, or office. It lets users quickly share files, printers, and internet access. LANs are a great choice for small businesses or individuals who want fast, local communication.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
A WAN connects networks over long distances, such as between cities or countries. Using public or private connections, like the internet, WAN links multiple LANs together. Large organizations often rely on a WAN to share data and resources between their locations.
LAN vs. WAN: The Simple Difference
| Aspect | LAN (Local Area Network) | WAN (Wide Area Network) |
| 1. Coverage Area | Works in a small area like a home, school, or single office. | Covers large areas like cities, countries, or even the whole world. |
| 2. Ownership | Usually owned and managed by one person or organization. | Managed by telecom or internet service providers. |
| 3. Performance & Speed | Offers high speed and wide bandwidth, so data moves fast. | Slower in speed and bandwidth compared to LAN. |
| 4. Cost & Maintenance | Low setup cost and simple to maintain. | High setup cost and harder to manage. |
| 5. Connection Type | Uses Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi. | Uses telephone lines, fiber optics, or satellite links. |
| 6. Security | More secure since access is limited to a small group. | Less secure due to wide coverage and multiple users. |
| 7. Reliability & Errors | Very reliable with fewer chances of data errors. | Less reliable and more prone to errors over distance. |
| 8. Latency (Delay) | Has very low latency; data travels quickly. | Higher latency since data moves over long distances. |
Detailed Comparison: LAN vs WAN
1. Coverage Area and Reach
A LAN (Local Area Network) works in a small area. Think of your home, a school, or an office building. It connects devices that are close to each other.
A WAN (Wide Area Network) spreads across a very large area. It links many LANs together across cities, regions, or even the whole world.
LANs connect devices within a small area, providing fast and stable communication. WANs, however, link devices or networks over long distances, connecting multiple locations but typically with slower speeds and more complexity.
2. Speed, Performance, and Delay
Because a LAN covers a short distance, it is very fast. Data moves almost instantly. You get smooth performance and high bandwidth for sharing large files.
A WAN is often slower. Data must travel long routes and pass through many other networks. This causes more delay (latency), and the connection is not always as stable.
LANs are fast and stable locally, while WANs link distant areas but may have slower speeds.
3. Cost, Setup, and Ownership
Setting up a LAN is a low-cost and easy process. It uses simple items like routers and Ethernet cables. One person or company usually owns and manages the entire LAN.
A WAN costs much more to build. It requires specialized equipment and may take several weeks to set up. Telecom companies or ISPs own and manage the WAN, so you share the control with them.
LANs are affordable and easy to manage. WANs cost more and are managed by providers.
4. Security and Risks
A LAN is a private network, so it is usually more secure. There are fewer risks since only a limited number of people are connected.
A WAN connects multiple networks over a vast geographical area. This raises the risk of security problems and errors. WANs must have significantly stronger security, such as firewalls.
LANs offer more security due to their limited number of users, while WANs require stronger protection.
5. Connection Types and Examples
LANs use simple technologies. This includes Ethernet cables or standard Wi-Fi. A good example is the network in your school or house.
WANs use advanced technologies to cover long distances. They might use phone lines, fiber optics, or satellites. The best example of a WAN is the Internet.
LANs use simple connection methods, while WANs need advanced technology for long distances.
Pros and Cons of LAN and WAN
Each type of network has strengths and drawbacks. Here is an overview of what makes LAN and WAN useful or challenging.
LAN (Local Area Network)
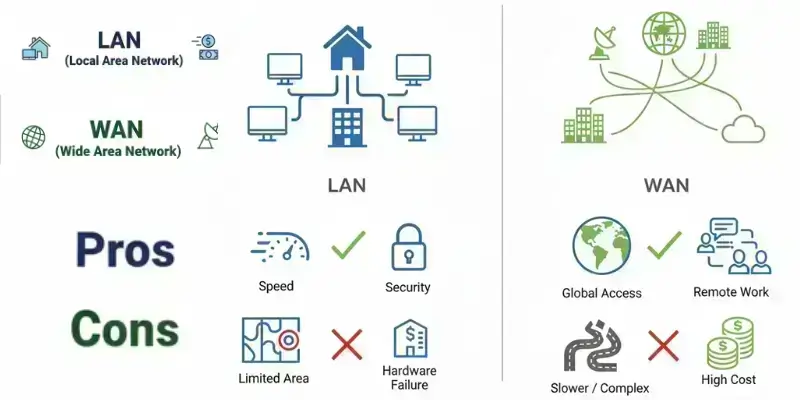
Pros
Fast connections for nearby devices
Easy to set up and manage
Low cost for small networks
Minimal delays when transferring files
Works well for gaming or streaming in one location
Cons
Limited to a small area
Not suitable for connecting multiple offices
Depends on Hardware failure affects all usersWide Area Network)
WAN (Wide Area Network)
Pros
Connects multiple locations over long distances
Supports large numbers of users
Enables remote work and communication
Scales easily for growing organizations
Access to the Internet and global services
Cons
Slower than LAN for local tasks
More expensive to set up and maintain
Can face downtime due to long-distance links
Similarities between LAN vs WAN
- Even though LAN and WAN work differently, they share several important features:
- Both connect devices, allowing users to share files and resources.
- Both can use wired or wireless connections depending on the setup.
- Both require network hardware, such as routers, switches, and modems.
- Both require security measures to protect data.
- Both help users communicate and collaborate efficiently.
Despite differences, both LANs and WANs connect devices for communication and collaboration.
Which One Should You Choose? LAN vs WAN
A LAN is suitable for a home, school, or small office network. It is fast, simple to set up, and cost-effective. Users experience smooth performance for gaming, streaming, or file sharing. Small teams or individuals will find it straightforward and dependable.
A WAN is ideal for large companies, remote teams, or organizations with multiple locations. It connects distant offices, supports global communication, and accommodates multiple users. Those needing network scalability and long-distance connectivity will benefit most.
Consider your primary needs. If speed and simplicity are important, LANs are a practical choice. To connect many people or locations, a WAN is preferable. Select the network type that matches your requirements for effective results.
Final Verdict
The key distinction is that LANs deliver local speed, privacy, and simplicity within confined spaces. WANs, on the other hand, are designed to interconnect networks over large distances, such as between cities or countries, offering greater reach but typically lower speed and added complexity. Select the network type based on your coverage and performance needs.
You May Also Like These Posts
Personal Area Network Security
What Is a Personal Area Network PAN
Personal Area Network Uses (PAN
Metropolitan Area Network Topologies
Types of Metropolitan Area Network
FAQs About LAN vs WAN
A LAN connects devices within a small area, such as a home or office. A WAN links multiple LANs across cities, countries, or even the world.
Yes! LANs often connect to a WAN to allow local devices to access the Internet or other distant networks.
LAN is faster because it covers a small area and has high bandwidth. WAN is slower due to long distances and multiple network connections.
Yes, but risks are lower because fewer devices are connected. Use strong passwords, firewalls, and antivirus software to stay safe.
WAN speed depends on distance, traffic, and the type of connection. Heavy use or long routes can cause delays.
Usually not. Most homes only need a LAN for Wi-Fi or wired connections. WAN is for businesses or multiple locations.
Verify that devices can connect and share files efficiently. If connections drop or speeds are slow, try restarting your router or checking the cables.
Yes. WAN enables employees in different cities or countries to connect and collaborate on a single network.
For LAN: routers, switches, and cables or Wi-Fi. For WAN: routers, modems, leased lines, and sometimes satellite or fiber connections.
For LAN: check cables, restart devices, or update network settings. For WAN: Contact your ISP, check the hardware, and ensure firewalls or VPNs aren’t blocking traffic.