Types of Wide Area Networks Every Business Should Understand
Published: October 13, 2025
Imagine you’re on an important video call, and suddenly your screen freezes. Or you’re trying to upload a file that just won’t go through. It’s frustrating — and often, the problem isn’t your device, but your network setup. Whether you’re working from home, running a business, or studying online, a weak connection can slow everything down. That’s why understanding the different types of Wide Area Network (WAN) is so important.
Each WAN type has strengths. Choosing the right one saves time, money, and stress. In this guide, we’ll explain each type step by step, in simple language—no tech background needed!
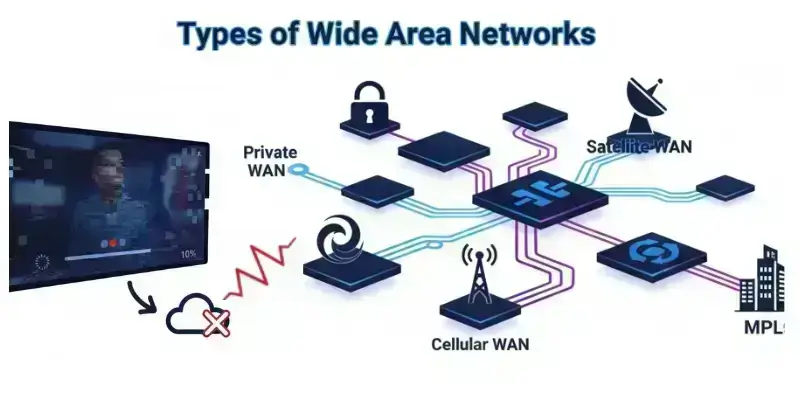
Types of WAN
Understanding WAN types helps you choose the right setup for business, education, or home use. Each offers different advantages.
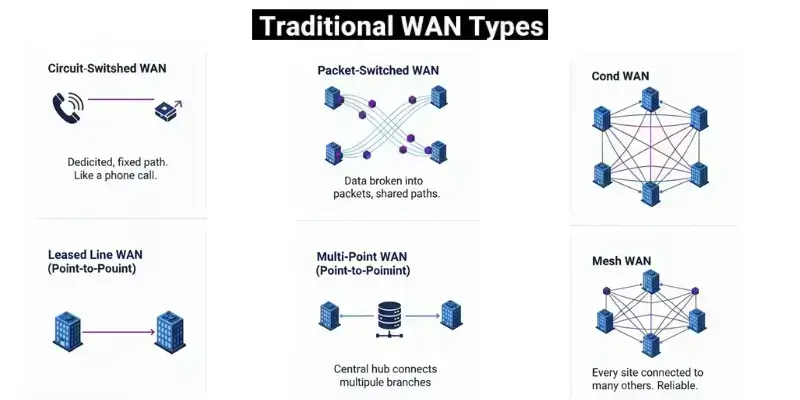
1. Traditional WAN Types
- Circuit-Switched WAN
- Packet-Switched WAN
- Leased Line WAN
- Switched WAN
- Point-to-Point (PPP) WAN
- Multi-Point WAN
- Mesh WAN
Circuit-Switched WAN
A Circuit-Switched WAN creates a special path between two locations that stays open until the conversation ends. No one else uses this path, so the connection stays strong and steady.
Features
Dedicated path for one connection at a time
Reliable, no dropouts during transmission
Works best for calls or live communication
Wastes bandwidth when not actively used
Takes time to set up before use
Examples
Traditional phone calls
Video calls that require stable links.
Banks and government offices
Who Should Use It
Use this if you want zero interruptions and can pay more for reliability.
Comparison
Unlike Packet-Switched WAN, it gives a dedicated path — more stable but more expensive.
Packet-Switched WAN
A Packet-Switched WAN divides data into small packets. Each packet travels separately and reassembles at the destination.
Features
Shares the same path among users
Works well for web browsing, email, and streaming
Finds new routes if one path is busy
Faster to start sending data.
Examples
Internet browsing
YouTube, WhatsApp, and online gaming
Who Should Use It
Ideal for home users or offices needing flexible and affordable internet.
Comparison
Cheaper and more flexible than Circuit-Switched WAN, but slightly less stable.
Leased Line WAN
A Leased Line WAN provides you with your own private “road” between two locations, ensuring fast and secure connectivity 24/7.
Features
Private connection only for you
Consistent high speed
Strong data protection
Always-on service
Guaranteed uptime from providers
Examples
Banks
Hospitals
Retail chains
Who Should Use It
Great for businesses that need fast, private, and reliable communication.
Comparison
Leased lines are faster and more secure than shared networks, but they cost more.
Switched WAN
A Switched WAN connects devices or offices over long distances using routers and switches that pick the fastest path.
Features
Dynamic routing for speed
Supports both old and new systems
Easily scales with your business.
Smart bandwidth use
Examples
MPLS networks
Frame Relay setups
Who Should Use It
Ideal for growing businesses that want reliability without fixed-line costs.
Comparison
Cheaper than dedicated WANs, but may experience slowdowns during heavy traffic.
Point-to-Point (PPP) WAN
PPP WAN connects two locations directly for secure, steady communication.
Features
Dedicated link between two sites
High security
Consistent speed
Low latency
Works with multiple protocols (IP, IPX, etc.)
Examples
Bank branches
Government offices
Who Should Use It
Best suited for organizations requiring private and secure data transfers.
Comparison
Unlike Frame Relay, PPP offers fully dedicated bandwidth.
Multi-Point WAN
A Multi-Point WAN connects multiple offices to a single central site through shared links.
Features
Connects three or more locations
Saves cost using one central hub
Easy to manage
Supports shared communication
Examples
Retail stores
Universities
Logistics companies
Who Should Use It
Perfect for growing businesses with multiple branches.
Comparison
More scalable and cost-friendly than a Point-to-Point WAN.
Mesh WAN
A Mesh WAN connects every site to several others. If one link fails, the others continue to run.
Features
Multiple data paths
High reliability
Strong performance
Easy to expand
Examples
Banks
Governments
Big tech companies
Who Should Use It
Best suited for large, critical networks that require nonstop uptime.
Comparison
More secure and flexible than a Point-to-Point WAN, but costlier.
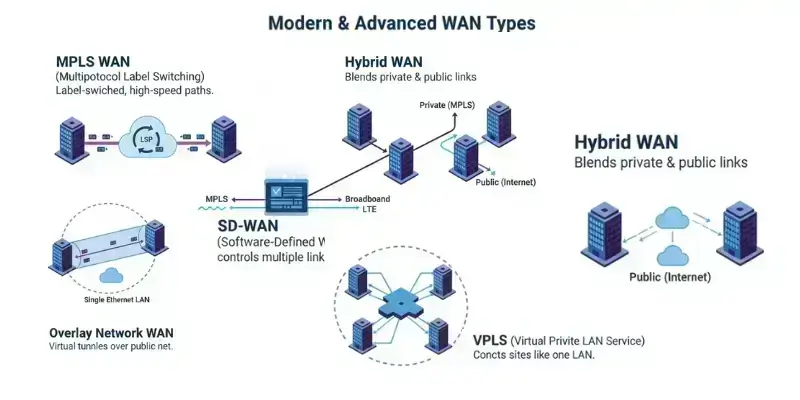
2. Modern & Advanced WAN Types
- MPLS WAN (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
- SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN)
- Hybrid WAN
- Overlay Network WAN
- VPLS (Virtual Private LAN Service)
MPLS WAN
MPLS WAN routes data using labels for faster delivery. It ensures smooth communication between branches with minimal delay.
Features
Low latency and high speed
Smart path selection
Prioritizes important data
Reliable and scalable
Examples
Banks
Telecom companies
Retail chains
Who Should Use It
Ideal for large businesses requiring stable, secure, and fast connections.
Comparison
More efficient than PPP for multi-site connectivity.
SD-WAN
SD-WAN uses smart software to manage connections across broadband, LTE, and MPLS links.
Features
Centralized control panel
Smart routing
Strong security
Easy scaling
Lower cost
Examples
Retail chains
Banks
IT firms
Who Should Use It
Best for multi-branch companies with cloud-based systems.
Comparison
More automated and affordable than traditional WANs.
Hybrid WAN
A Hybrid WAN combines private and public networks to achieve the optimal balance of performance, security, and cost.
Features
Uses both MPLS and the Internet
Smart traffic routing
Reduces cost
Boosts reliability
Examples
Retail chains
Banks
Global corporations
Who Should Use It
Ideal for businesses that utilize both cloud and local systems.
Comparison
Offers both the speed of private lines and the flexibility of the internet.
Overlay Network WAN
Overlay WAN builds a virtual network on top of an existing one, using encrypted tunnels instead of physical lines.
Features
Works over the existing Internet
Encrypted and private
Cloud-friendly
Easy to scale
Examples
Google Cloud VPN
Microsoft Azure WAN
Who Should Use It
Ideal for growing companies with multiple offices.
Comparison
More flexible and cheaper than direct physical connections.
VPLS (Virtual Private LAN Service)
VPLS WAN links multiple offices into a single large virtual network — just as if they were in the same building.
Features
High-speed Ethernet connection
Secure and private
Full mesh communication
Low delay
Examples
Global firms
Universities
Financial companies
Who Should Use It
Ideal for organizations that require seamless communication across multiple locations.
Comparison
Connects many sites, unlike a Point-to-Point WAN.
3. Internet-Based WAN Types
- Public WAN
- Private WAN
- Cloud-Based WAN
- VPN WAN
- Dedicated Internet Access (DIA)
- Broadband Internet WAN
Public WAN
A Public WAN uses the internet to connect users worldwide. It’s the most common and affordable option.
Features
Uses public broadband or fiber
Easy to set up
Supports VPNs
Low cost
Examples
Google Workspace
Remote learning systems
Who Should Use It
Best for small offices, schools, and startups.
Comparison
Cheaper than a Private WAN but less secure.
Private WAN
A Private WAN connects multiple sites through secure, dedicated links owned by one organization.
Features
Exclusive network
Strong security
Fast and reliable
Custom design
Examples
Banks
Hospitals
Retail companies
Who Should Use It
Ideal for large businesses that handle sensitive data.
Comparison
More private and stable than the Public WAN, but costs more.
Cloud-Based WAN
A Cloud-Based WAN connects offices and users through cloud services, rather than relying on hardware.
Features
Central control panel
Easy to expand
Cost-effective
High security
Examples
Google Cloud WAN
Cisco Meraki WAN
Who Should Use It
Ideal for cloud-first businesses and remote teams.
Comparison
More scalable than traditional physical networks.
VPN WAN
A VPN WAN establishes a secure, private tunnel over the internet, allowing users to connect safely.
Features
Uses encryption for security
Remote access from anywhere
Cost-effective
Works with firewalls
Examples
Remote workers
Global companies
Who Should Use It
Great for small and medium businesses needing security at a low cost.
Comparison
Safer than Public WAN but cheaper than leased lines.
Dedicated Internet Access (DIA) WAN
DIA WAN provides a private, high-speed internet connection that’s not shared with anyone.
Features
Guaranteed bandwidth
Equal upload/download speed
Reliable uptime
Strong security
Examples
Banks
IT firms
Schools
Who Should Use It:
For businesses that rely on stable, fast internet 24/7.
Comparison
More consistent than shared broadband but higher in price.
Broadband Internet WAN
A Broadband WAN uses DSL, fiber, or cable to connect sites with high-speed internet.
Features
Fast upload/download speeds
Always on
Easy setup
Wide availability
Examples
Schools
Home offices
Small companies
Who Should Use It
Perfect for homes or small offices wanting affordable speed.
Comparison
Cheaper than private links but shared among users.
4. Wireless & Satellite WAN Types
- Wireless WAN (WWAN)
- Cellular WAN
- Satellite WAN
Wireless WAN (WWAN)
A Wireless WAN connects devices using cellular networks like 4G or 5G — no cables needed.
Features
Wide coverage
Quick setup
Supports mobile teams
Works as a backup for wired lines
Examples
ATMs
Delivery vehicles
Rural schools
Who Should Use It
Ideal for mobile teams and remote areas.
Comparison
More flexible than wired WANs, but depends on signal quality.
Cellular WAN
A Cellular WAN connects through mobile networks using SIM-based devices.
Features
4G/5G speed
High mobility
Easy setup
Reliable connectivity
Examples
Buses offering Wi-Fi
Field workers
Remote kiosks
Who Should Use It
Perfect for moving or remote setups.
Comparison
More mobile but less consistent than wired WANs.
Satellite WAN
A Satellite WAN connects remote areas using signals from orbiting satellites.
Features
Works anywhere on Earth
Great for rural or sea areas
Slight delay possible
Reliable during disasters
Examples
Airlines
Oil rigs
Disaster response teams
Who Should Use It
Best for remote or hard-to-reach regions.
Comparison
No cables are needed, but it is slightly slower than wired WANs.
5. WAN Technologies & Protocols
These aren’t WAN types but important technologies that support them.
- TCP/IP Protocol Suite
- Packet Switching
- Packet over SONET/SDH (PoS)
- ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode)
- Router (Supporting Device)
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
The TCP/IP Protocol Suite is the language of the Internet — it defines how data is sent, received, and reassembled.
Features
Divides data into packets
Reliable and global
Works across all devices
Handles errors automatically
Examples
Web browsing (HTTP)
Email (SMTP)
File transfers (FTP)
Who Should Use It
Essential for all internet-connected systems.
Comparison
Simpler and more practical than older OSI models.
Packet Switching
Packet Switching breaks data into small pieces and sends them through the fastest available routes.
Features
Smart routing
Efficient bandwidth use
Auto recovery for lost data
Examples
YouTube
Internet browsing
Who Should Use It
Best for internet users and streaming platforms.
Comparison
More efficient than circuit switching.
Packet over SONET/SDH (PoS)
PoS sends IP packets over fiber-optic lines for fast, stable data transmission.
Features
High speed
Low delay
24/7 uptime
Strong error correction
Examples
ISPs
Banks
Research networks
Who Should Use It
Ideal for telecom and enterprise networks.
Comparison
Faster and more reliable than Frame Relay.
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode)
ATM transmits data in small, fixed cells for smooth performance.
Features
Fixed-size data cells
Real-time voice and video
Guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS)
Examples
Banks
Universities
Telecom systems
Who Should Use It
Best for organizations needing delay-free video or voice communication.
Comparison
Faster and more controlled than Frame Relay, but costlier.
Router (Supporting Device)
A Router connects different networks and directs data to its destination efficiently.
Features
Connects LAN and WAN
Manages IP addresses
Offers Wi-Fi and wired connections
Includes security controls
Examples
Home routers
Office routers
ISP routers
Who Should Use It
Every home or business needs multiple device connections.
Comparison
Routers link networks, while switches connect devices within one network.
Comparison Table of Types of Wide Area Network (WAN
Comparing the different Types of Wide Area Network (WAN) helps you choose the best option for your needs. Each type has unique features, advantages, and use cases. This quick table shows how they differ, allowing you to make an easy decision.
| WAN Type | Key Features | Best Use | Pros | Cons |
| Circuit-Switched WAN | Dedicated path between sites | Voice or video calls | Reliable, stable connection | Wastes bandwidth when idle |
| Packet-Switched WAN | Data sent in packets | Internet use, streaming | Flexible, fast data flow | Slightly less stable |
| Leased Line WAN | Private, always-on line | Banks, hospitals | Secure, consistent speed | Expensive setup |
| Switched WAN | Dynamic routing | Growing networks | Scalable and efficient | May slow during traffic |
| PPP WAN | Direct link between two sites | Secure communication | Stable and low latency | Limited to two sites |
| Multi-Point WAN | Central hub with branches | Multi-office setup | Cost-saving and scalable | Shared bandwidth |
| Mesh WAN | Many interlinked nodes | Critical systems | Highly reliable and flexible | Complex and costly setup |
| MPLS WAN | Label-based routing | Enterprises | Fast and low delay | Complex setup |
| SD-WAN | Software-managed links | Cloud-based firms | Smart routing and secure | Needs setup expertise |
| Hybrid WAN | Mix of public & private | Multi-branch orgs | Cost-effective and flexible | Needs management |
| VPN WAN | Encrypted internet tunnel | Remote workers | Secure and private | Slightly slower speed |
| Cloud-Based WAN | Internet + cloud control | Cloud-first companies | Easy to expand | Depends on ISP |
| Wireless WAN | Cellular-based network | Mobile teams | Flexible and fast | Signal issues |
| Satellite WAN | Signal via satellite | Remote areas | Works anywhere | Slight Delay |
How to Choose the Right Type of Wide Area Network (WAN)
Now that we’ve explored all the types of Wide Area Networks (WANs), the next step is to determine which one best fits your needs. Choosing the right WAN can boost your speed, strengthen your data security, and save you from future headaches. Let’s break it down simply and clearly.
1. For Small Businesses or Startups
If you’re just starting out or running a small office, focus on simplicity and cost efficiency.
Best Choices: VPN, WAN, or Broadband WAN
These options are affordable and easy to set up. You’ll get a decent connection for emails, online meetings, and cloud tools like Google Workspace.
Expert Tip
According to recent reports, approximately 45% of small businesses utilize VPN WANs for secure remote work connections — a safe and budget-friendly option.
2. For Growing or Multi-Branch Companies
If you have multiple branches or remote offices, go for a WAN that’s reliable and flexible.
Best Choices: SD-WAN or Hybrid WAN
These are modern, software-based options that enable you to manage all your locations from a single control panel. They strike a perfect balance between speed, security, and cost.
Expert Recommendation
Studies show over 60% of enterprises have shifted to SD-WAN because it cuts costs by up to 40% while improving network performance.
3. For Large Enterprises or Banks
Large organizations handle sensitive data and can’t afford downtime. They need strong, stable, and private connections.
Best Choices: MPLS WAN or Leased Line WAN
These offer dedicated bandwidth, guaranteed uptime, and enterprise-grade security.
Expert Insight
Most financial institutions still rely on MPLS networks due to their unmatched reliability and security compliance standards.
4. For Remote Areas or Mobile Operations
Working in rural regions or managing mobile teams? You need something that doesn’t depend on cables.
Best Choices: Wireless WAN or Satellite WAN
These provide coverage where wired connections aren’t possible.
Pro Tip
Satellite WANs have undergone significant improvements with the introduction of new technologies, such as Starlink, now offering speeds of 100–150 Mbps even in remote areas.
5. For Cloud-Based or Digital Businesses
If your work revolves around online tools, cloud storage, and remote access, you’ll want a fast, secure, and flexible network.
Best Choices:Cloud-Based WAN or SD-WAN
They connect seamlessly with services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Industry Trend
As of 2025, 75% of digital-first companies have adopted SD-WAN or Cloud WAN to manage global teams efficiently.
Recommendation
If you’re unsure where to start, begin with SD-WAN. It’s the modern all-rounder — smart, secure, and budget-conscious. You can later combine it with MPLS or Cloud WAN as your needs grow.
Quick Tip
Always consider your budget, data sensitivity, and location when making a choice. A well-matched WAN doesn’t just connect your offices — it keeps your business running smoothly.
Conclusion
So folks, we’ve covered everything about the types of Wide Area Network (WAN) — from traditional setups like Circuit-Switched and Leased Lines to modern options like SD-WAN, Cloud-Based WAN, and Satellite WAN. Each type serves a unique purpose, whether you’re running a small startup, managing multiple offices, or connecting remote teams across the globe.
As an expert, my recommendation is simple: don’t rush your choice. The right type of Wide Area Network can make your business faster, safer, and more reliable. If you’re unsure, start with SD-WAN — it’s flexible, affordable, and perfect for most modern setups.
The world of networks is changing fast, buddies. New technologies like 5G, AI-driven routing, and cloud connectivity are reshaping how we stay connected. Keep exploring, keep upgrading, and stay informed — because the future of WAN is all about smarter, stronger, and simpler connections.
FAQs About Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) connects computers and offices across long distances, even spanning cities or countries. It uses routers, cables, and sometimes satellites to send data between locations. Think of it as a big bridge that links smaller local networks (LANs) together.
The main types include Leased Line WAN, MPLS, SD-WAN, VPN WAN, and Satellite WAN. Each type offers different speed, security, and cost levels. Businesses often use SD-WAN today because it’s flexible and cloud-friendly.
For small businesses, VPN, WAN, or Broadband WAN is the best option. They’re easy to set up, secure enough for daily work, and don’t cost much. Many startups utilize VPNs because they enable teams to work securely from anywhere.
A LAN (Local Area Network) connects devices within a single building, such as your home or office. A WAN, on the other hand, links multiple LANs across different locations. In short, LAN is local — WAN is global.
Yes, the Internet is the largest WAN in the world. It connects millions of private, public, and business networks worldwide. Every time you send an email or join a video call, you’re using WAN technology.
Companies love SD-WAN because it’s fast, secure, and cost-efficient. It helps control network traffic through software instead of hardware. In 2025, over 60% of global enterprises are expected to utilize SD-WAN, as it simplifies cloud connectivity.
If you’re in a remote location, go for Satellite WAN or Wireless WAN. They don’t need cables and can reach areas with limited infrastructure. Services like Starlink now make satellite internet faster and more reliable than ever.
Consider your budget, the number of offices, and your data security needs. Small teams can use VPN WANs, while large companies should consider SD-WAN or MPLS. Always choose a WAN that supports your growth and keeps your data safe.